The automobile industry is undergoing a transformative phase, with autonomous vehicles (AVs) at the forefront of this evolution. These self-driving marvels promise to revolutionize mobility, improve safety, and redefine the way we interact with transportation systems. This post delves deep into the world of autonomous vehicles, exploring their technology, benefits, challenges, and the bright future they promise.
What Are Autonomous Vehicles?
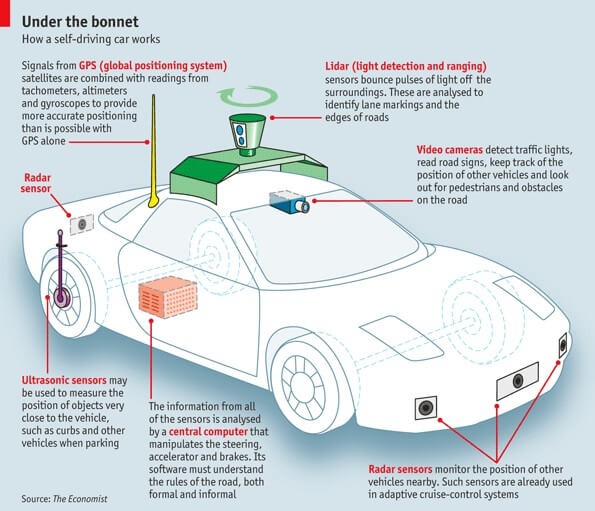
Autonomous vehicles, commonly known as self-driving cars, are equipped with advanced systems that allow them to operate without human intervention. These vehicles rely on a combination of hardware and software, such as sensors, cameras, artificial intelligence (AI), and machine learning, to navigate roads, interpret traffic signals, and make driving decisions.Autonomous vehicles are cars that operate without human intervention. Equipped with cutting-edge technologies like LiDAR, radar, cameras, and advanced machine learning algorithms, these vehicles can navigate roads, recognize obstacles, and make driving decisions in real time.
They are categorized into six levels of autonomy, as defined by the Society of Automotive Engineers (SAE):
- Level 0: No automation; the driver has full control.
- Level 1: Driver assistance systems, such as adaptive cruise control.
- Level 2: Partial automation, where the car can control steering and acceleration but the driver must remain engaged.
- Level 3: Conditional automation, allowing the vehicle to manage most tasks under certain conditions, though human intervention is still needed.
- Level 4: High automation, where the vehicle can operate independently in specific conditions without human input.
- Level 5: Full automation, where no human intervention is required in any driving scenario.
The Key Technologies Behind Autonomous Vehicles
The development of AVs involves a symphony of sophisticated technologies working together seamlessly. Let’s explore the major components:
1. Artificial Intelligence (AI)
AI is the brain behind self-driving cars. It processes data from sensors, interprets the environment, and makes real-time decisions to ensure safe and efficient driving. AI algorithms are trained on vast datasets to recognize objects, predict movements, and respond accordingly.
2. LiDAR and Radar
- LiDAR (Light Detection and Ranging): It uses laser pulses to create detailed 3D maps of the environment, allowing the vehicle to “see” its surroundings.
- Radar: Radar systems detect objects and measure their speed and distance, even in adverse weather conditions.
3. Cameras
High-resolution cameras capture images and videos, helping the car identify road signs, lane markings, and obstacles.
4. Sensor Fusion
This technology combines data from multiple sensors, creating a comprehensive view of the environment. Sensor fusion enhances accuracy and reliability, ensuring smooth operation.
5. Connectivity (V2X Communication)
- Vehicle-to-Vehicle (V2V): Enables cars to share information, such as speed and position, to avoid collisions.
- Vehicle-to-Infrastructure (V2I): Connects vehicles to traffic signals, road signs, and other infrastructure for better traffic management.
6. Advanced Computing
Powerful onboard computers process vast amounts of data in milliseconds, enabling the vehicle to make complex decisions instantaneously.
The Benefits of Autonomous Vehicles
The rise of autonomous vehicles heralds a new era of convenience, safety, and efficiency. Here are some key benefits:
1. Enhanced Road Safety
Human error is a leading cause of road accidents. Autonomous vehicles eliminate distractions, fatigue, and impaired driving, significantly reducing accidents.
2. Improved Traffic Management
Self-driving cars use real-time data to optimize routes, reduce congestion, and enhance traffic flow. This can save time and fuel for commuters.
3. Increased Accessibility
Autonomous vehicles offer mobility solutions for the elderly, disabled, and those unable to drive, promoting inclusivity.
4. Environmental Benefits
Optimized driving patterns reduce fuel consumption and emissions, contributing to a cleaner environment.
5. Cost Savings
Though the initial investment is high, autonomous vehicles reduce long-term costs by minimizing accidents, fuel usage, and wear and tear.
Challenges and Roadblocks
Despite their immense potential, autonomous vehicles face several challenges:
1. Regulatory Hurdles
Governments worldwide must establish safety standards and liability laws for AVs, which can be a slow and complex process.
2. Ethical Dilemmas
Self-driving cars may encounter situations requiring moral decisions, such as choosing between two harmful outcomes. Addressing these dilemmas is a significant challenge.
3. Cybersecurity Risks
As connected devices, autonomous vehicles are vulnerable to hacking. Robust cybersecurity measures are essential to ensure safety.
4. High Costs
Developing and implementing AV technology involves significant costs, which can make these vehicles expensive for consumers.
5. Public Acceptance
Many people are hesitant to trust self-driving cars, fearing malfunctions or loss of control. Building public confidence is crucial for widespread adoption.
Real-World Applications
Autonomous vehicles have a wide range of applications, transforming various sectors:
1. Ride-Sharing Services
Companies like Waymo and Uber are developing self-driving fleets, offering convenient and cost-effective transportation.
2. Freight and Logistics
Autonomous trucks can revolutionize the logistics industry by ensuring timely deliveries and reducing labor costs.
3. Public Transportation
Self-driving buses and shuttles are being tested in cities, promising safer and more efficient public transport.
4. Agriculture
Autonomous tractors and machinery enhance productivity and reduce labor dependency in farming.
5. Healthcare
Self-driving ambulances can provide quicker response times and safer transportation for patients.
The Road Ahead
The future of autonomous vehicles looks promising, with rapid advancements in technology and increasing investments from automakers and tech companies. Here are some trends shaping the future:
1. Integration with Smart Cities
AVs will seamlessly integrate with smart city infrastructures, improving traffic management and energy efficiency.
2. Shared Mobility
The rise of car-sharing and subscription-based models will make autonomous vehicles more accessible.
3. Electric and Autonomous Synergy
Combining electric vehicles (EVs) with autonomy will amplify the environmental benefits, accelerating the transition to sustainable transportation.
4. Autonomous Flying Cars
Companies like Uber Elevate are exploring the possibility of autonomous flying taxis, taking mobility to new heights.
Conclusion
Autonomous vehicles represent the pinnacle of innovation in the automobile industry. By combining advanced technology with sustainable practices, they promise to reshape the way we travel and interact with the world around us. While challenges remain, the potential benefits far outweigh the obstacles.
As we stand on the cusp of this revolution, one thing is certain: autonomous vehicles are not just a technological marvel; they are a symbol of progress, paving the way for a safer, greener, and more connected future.
The journey towards autonomy is well underway, and its destination promises to be nothing short of extraordinary.